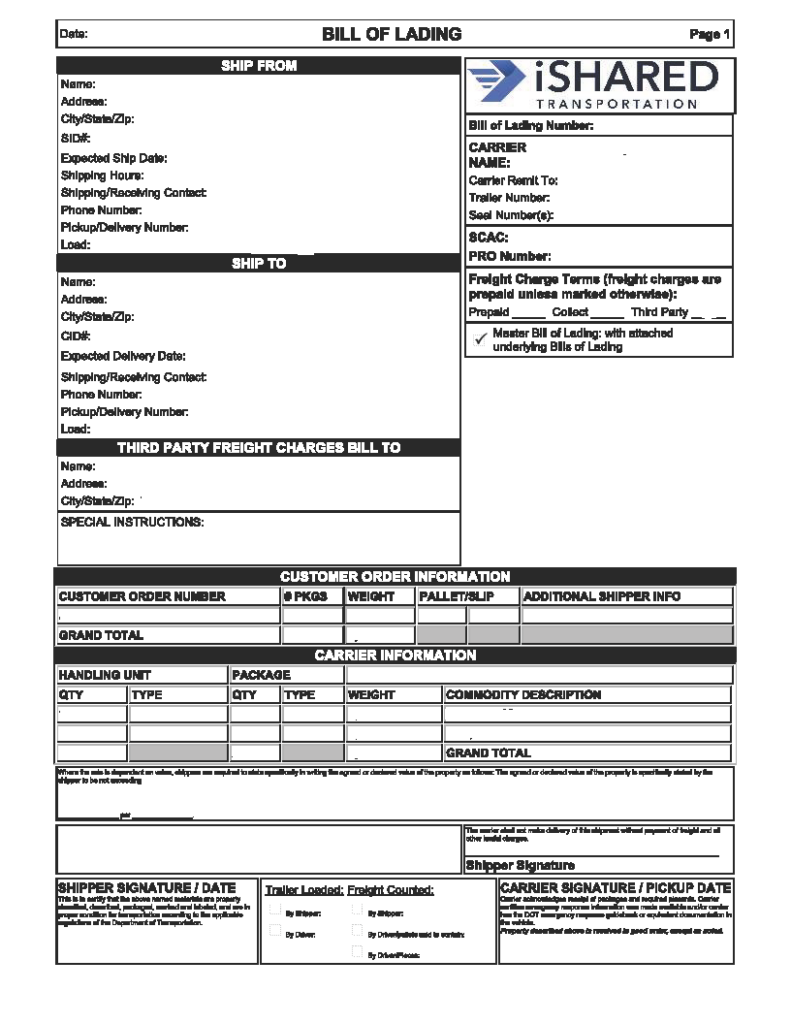
In the complex world of logistics, where goods travel vast distances and change hands multiple times, the Bill of Lading (BOL) stands as a crucial document. UPS’s simple definition is clear: “A legally binding document issued by a carrier that authorizes the carrier to transport goods on their behalf.” However, this piece of paperwork is more than just a receipt; it is a detailed roadmap that provides essential information about the shipment, its journey, and the parties involved. Understanding how to read a Bill of Lading is a fundamental skill for anyone involved in shipping and receiving goods. Our team at iShared Transportation will break down the key components of a Bill of Lading and explain how to interpret this vital document.
1. **Header Information: **
The top section of the Bill of Lading typically includes the names and addresses of the shipper (the party sending the goods), the consignee (the party receiving the goods), and the carrier (the entity responsible for transporting the goods). This section also indicates the date of issuance and the BOL number, a unique identifier for the document.
2. **Description of Goods: **
A detailed description of the shipped goods, including information such as the quantity, weight, dimensions, and packaging type. This section is crucial for both the shipper and the consignee to ensure that the correct items are being transported.
3. **Origin and Destination: **
The Bill of Lading specifies the origin and destination of the shipment, outlining where the goods are being picked up and where they are to be delivered. This information is vital for coordinating the logistics chain and ensuring timely delivery.
4. **Carrier Information: **
Details about the carrier, including their name, contact information, and any special instructions related to the transportation of goods, are clearly outlined. This section helps both the shipper and consignee stay informed about the responsible party for the duration of the shipment.
5. **Special Instructions and Terms: **
Any special handling instructions or terms of the agreement between the shipper and the carrier are included in this section. This may include details about the mode of transport, temperature requirements, or any other specific conditions for the safe delivery of the goods.
6. **Charges and Payments: **
The Bill of Lading also provides information about freight charges, whether prepaid or collect. It serves as a reference for financial transactions related to the shipment.
7. **Signatures and Dates: **
Finally, the Bill of Lading is not complete without the signatures of the shipper, carrier, and the consignee. These signatures confirm that the goods have been received in the stated condition and serve as a legal acknowledgment of the terms and conditions outlined in the document.
In the words of our CEO, Kyle Ingraham, “The Bill of Lading is more than a document; it’s a commitment to the seamless movement of goods and a testament to the collaboration that powers our global supply chain.”
In the intricate web of global trade and logistics, the ability to decipher a Bill of Lading is a valuable skill. This document encapsulates the entire journey of shipped goods, from their origin to their final destination. By understanding the components of a Bill of Lading, businesses can ensure the smooth flow of their supply chain, reduce the risk of errors, and foster a more efficient and reliable transportation process.